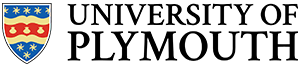A signal with a value that can take any value, typically between two limits. We say such values are ‘continuous’, i.e. there are no intervals or steps. An example is shown below. Here a signal ![]() represents a voltage that is changing with time
represents a voltage that is changing with time ![]() . The signal can take any value such that
. The signal can take any value such that ![]() , where
, where ![]() and
and ![]() are the lower and upper limits.
are the lower and upper limits.
All electrical systems are ultimately analogue when you look closely enough. I contrast, digital systems employ high-gain amplifiers to switch between two extremes very quickly, giving the impression of working in only two states.