A switch-case is used for flow control when you are testing the same variable for equality.
switch (expression) {
<declarations>
case constant:
statements
break;
case constant:
statements
break;
default:
statements
break;
}
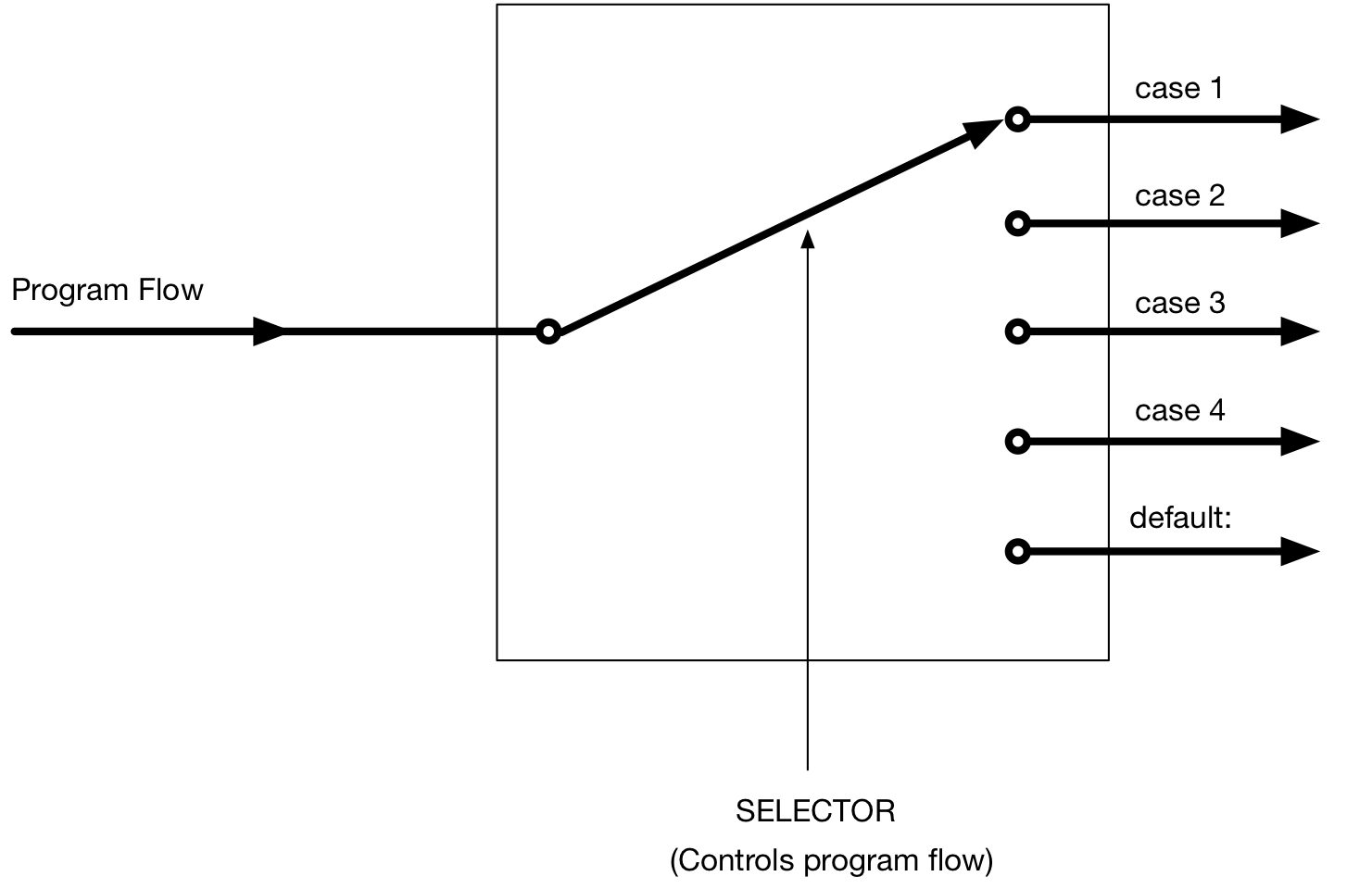
The term ‘expression’ above refers to a variable under test. From the diagram below, it is the selector that is used to determine the flow of code within the switch-case statement.
Consider the following example:
int iResponse;
puts("Please select:");
puts("0 - Sales");
puts("1 - Opening hours");
puts("2 - Repairs");
puts("3 - Complaints");
puts("4 - Anything else");
scanf("%d", &iResponse);
if (iResponse == 0) {
puts("Please wait for a sales advisor");
playAnnoyingMusic(5);
redirect(123);
} else if (iResponse == 1) {
puts("We are open 24Hrs 7 days a week");
redirect(0);
} else if (iResponse == 2) {
puts("Please wait while we redirect you");
playAnnoyingMusic(25);
redirect(124);
} else if ((iResponse == 3) || (iResponse == 4)) {
puts("Please wait while we redirect you");
playAnnoyingMusic(60);
redirect(0); //very cynical
} else {
puts("Returning to main menu");
playAnnoyingMusic(5);
redirect(0); //very cynical
};
Note how it is the same variable being tested each time. The equivalent code with a switch-case is as follows:
int iResponse;
puts("Please select:");
puts("0 - Sales");
puts("1 - Opening hours");
puts("2 - Repairs");
puts("3 - Complaints");
puts("4 - Anything else");
scanf("%d", &iResponse);
switch (iResponse) {
case 0:
puts("Please wait for a sales advisor");
playAnnoyingMusic(5);
redirect(123);
break;
case 1:
puts("We are open 24Hrs 7 days a week");
redirect(0);
break;
case 2:
puts("Please wait while we redirect you");
playAnnoyingMusic(25);
redirect(124);
break;
case 3:
case 4:
puts("Please wait while we redirect you");
playAnnoyingMusic(60);
redirect(0); //very cynical
break;
default:
puts("Returning to main menu");
playAnnoyingMusic(5);
redirect(0); //very cynical
break;
};
Notes:
- Each evaluation must be exclusive
- Use break to avoid falling through into the next case (common error)
- Multiple conditions can be handled by writing separate case statements without a break.
- default (optional) is the catch-all if none are matched